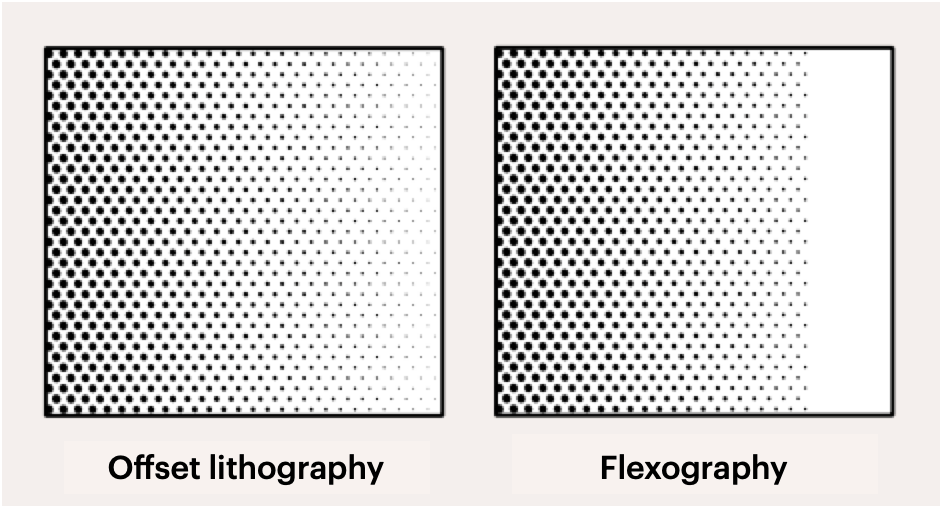
Printing with flexographic technology involves directly applying ink to a printing plate, which is then transferred to the substrate. The printing plate is made of a layer of rubber that has been cured or hardened to the correct thickness. The rubber layer is then applied over the surface of the printing cylinder and inked with a flexible roller or paper web.
The inked image on the printing plate is then pressed onto the substrate. The most common method used to print a design on a substrate is by means of a printing press.
Importance of ink drying process of flexo inks
Ink drying method plays an important role in the quality of printed materials. The reason for this is that the ink must be perfectly dried in order to produce a perfect print. A printing ink’s structure should be adequate for rapid drying and anchoring on the substrate after printing, while avoiding drying on the press during operation or short standstills.
Slow drying will result in blurred images because the ink spreads over the paper. When it dries quickly, it won’t spread on the paper and will form a clear image.
Between the last printing unit and winding, the drying process must be completed. Printing inks have different drying mechanisms depending on the following factors:
1. Method of printing (offset, gravure, flexography, etc.)
2. The type of printing ink (liquid, paste, water or organic solvent-based, radiation-cured, etc.)
3. Speed of printing machines.
4. Printing materials substrates (paper, foils, plastics, etc.)
5. The type of the printed product (packaging printing, commercial printing, etc.)
6. The characteristics of the dryer systems (hot air, cured systems, IR, etc.,)
These are three general Drying methods for printing inks in flexography.
Evaporation Drying
Ink compositions contain solvents that quickly evaporate after printing and separate from the ink. Heaters are used to accomplish this process during production.
Absorption Drying
The carrier viscosity of the printing ink determines this type of drying.
As the ink droplets penetrate the carrier, the carrier is dewatered as the ink droplets absorption occurs.
Ultraviolet (UV) Curing
UV inks are cured through a chemical polymerization reaction triggered by UV radiation, so only UV-curing machines can be used to print with them.
There are many applications for UV curing inks, including labels, decorative films, protective films, decorative foils, and packaging materials.