As the flexographic printing industry advances, so does the demand for efficient, uninterrupted workflows that maximize productivity. One of the most effective solutions to support seamless operations in high-speed printing is the use of automatic splicing systems. These systems allow continuous substrate feeding without the need to stop the press, saving valuable time, reducing material waste, and ensuring uninterrupted production. This article provides a comprehensive look into the function, benefits, and technical aspects of automatic splicing systems in flexography.
Introduction to Automatic Splicing Systems
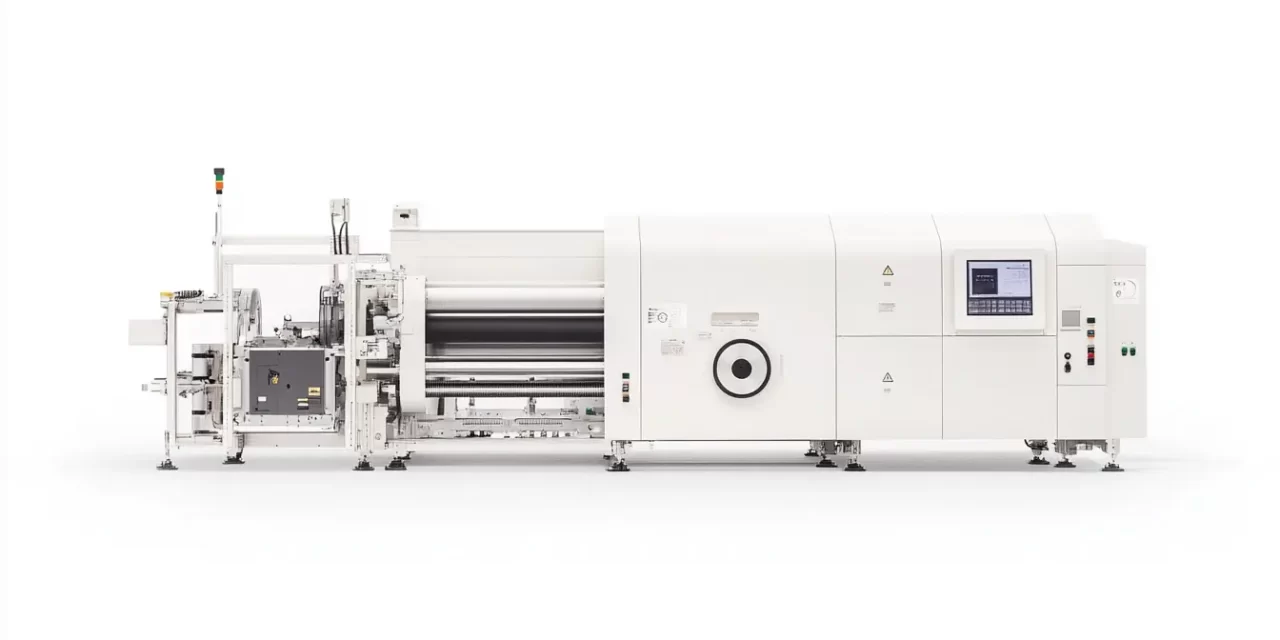
Automatic splicing systems are an essential tool in modern flexographic printing setups. They facilitate the smooth transition from one roll of substrate to another without halting the printing process, eliminating the need for manual roll changes. By automating the splicing process, these systems significantly reduce downtime and material waste, allowing printers to maintain continuous operations.
Importance of Automatic Splicing in Flexographic Printing
Flexography, especially in packaging and high-volume production, requires continuous runs to achieve the high efficiency and output expected by clients. Traditional manual splicing or roll changing disrupts production flow and increases waste, affecting both productivity and profitability. Automatic splicing addresses these challenges by ensuring that substrate rolls are joined seamlessly, preventing pauses in the print process and optimizing the overall efficiency of the operation.
How Automatic Splicing Systems Work
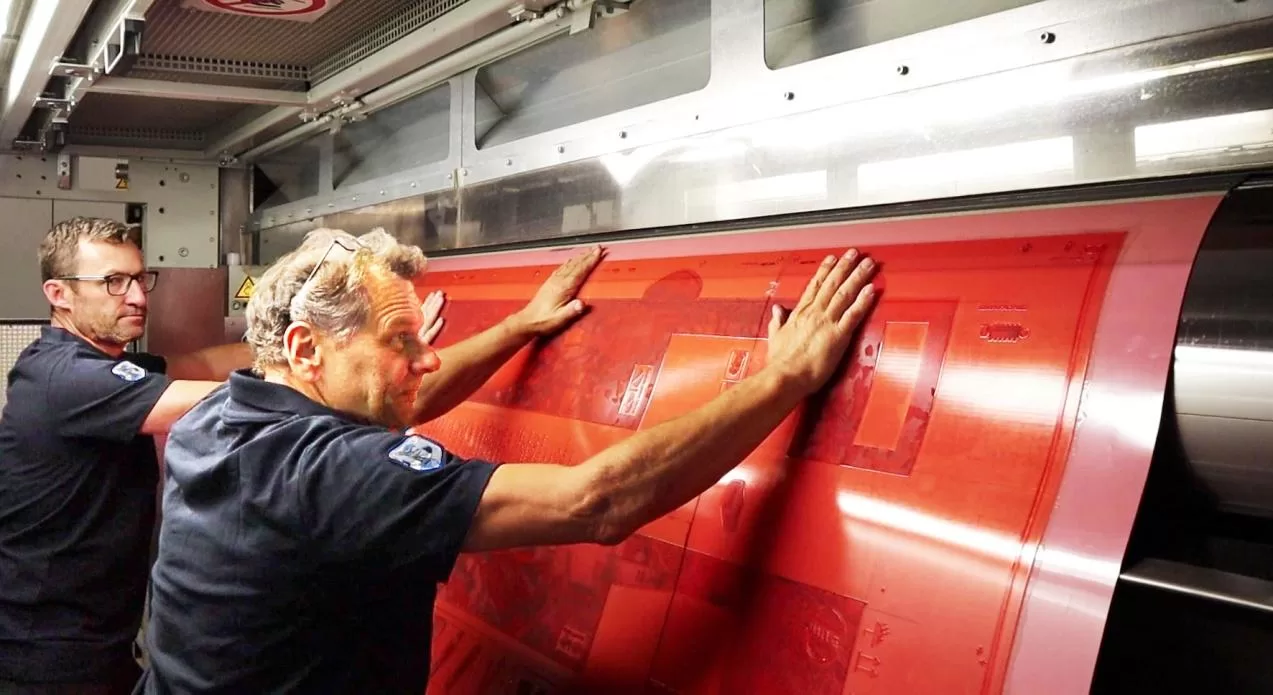
Automatic splicing systems work by attaching a new roll of substrate to the end of an expiring roll without interrupting the printing process. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Sensor Detection: Sensors detect when the current roll is nearing its end and triggers the splicing mechanism.
- Preparation of New Roll: The system preps the new roll by aligning it with the remaining substrate from the current roll.
- Adhesive Application: Adhesive is applied to ensure that the two substrate ends bond securely.
- Joining Process: The two ends of the substrate are joined seamlessly, and the expiring roll is ejected, allowing the new roll to continue feeding the press.
By automating these steps, automatic splicing systems reduce the need for operator intervention and maintain the printing process without any interruption.
Types of Automatic Splicing Systems in Flexography
Zero-Speed Splicing Systems
Zero-speed splicers stop the motion of the web momentarily to complete the splice but do not require the entire press to stop. This approach allows for precise splicing without slowing down the overall production speed, as the splice is completed within seconds.
Flying Splicing Systems
Flying splicing systems allow the new roll to join the running substrate without stopping or slowing down the press. This type of system is beneficial in ultra-high-speed production environments where even minimal pauses can impact efficiency.
Lap and Butt Splicing Systems
- Lap Splicing: The ends of the substrate are overlapped and bonded with adhesive. Lap splicing is simple and effective for most applications but can create a slight thickness variation at the splice point.
- Butt Splicing: The ends of the substrate meet precisely edge-to-edge, producing a flat, seamless joint. This method is particularly suitable for high-quality printing where uniform substrate thickness is essential.
Key Components of Automatic Splicing Systems
Sensors
Sensors detect the diameter of the remaining roll and signal when the roll is near its end, prompting the splicing mechanism to initiate.
Roll Preparation Unit
This unit holds the new roll and aligns it with the current roll, applying the adhesive to ensure a secure bond between the two rolls.
Control System
The control system orchestrates the splicing process, monitoring sensor data and controlling motor functions to ensure precise, timely splicing without any manual intervention.
Drive and Tension Control
To prevent misalignment and substrate breakage, splicing systems incorporate tension control mechanisms that maintain consistent tension throughout the splicing process, ensuring smooth substrate feed.
Advantages of Automatic Splicing Systems
Minimized Downtime
Automatic splicing enables continuous operation by eliminating the need for manual roll changes. This minimizes downtime, allowing print runs to proceed uninterrupted, thus improving overall production speed.
Reduced Material Waste
By ensuring precise joining of substrates, splicing systems reduce the likelihood of material wastage caused by misalignment or substrate tearing.
Enhanced Operator Efficiency
With splicing fully automated, operators can focus on monitoring other aspects of production, such as color accuracy and registration, rather than managing roll changes.
Consistent Product Quality
Automatic splicing systems maintain the uniform tension and substrate alignment necessary for consistent print quality across long runs, a significant benefit in high-quality flexographic printing applications.
Applications of Automatic Splicing Systems in Flexography
Automatic splicing systems are essential in industries requiring high-speed flexographic printing, including:
- Flexible Packaging: High-speed production of food packaging, pouches, and wraps benefits greatly from uninterrupted workflows enabled by splicing systems.
- Label Printing: The precision required in label printing demands consistent tension and alignment, making automatic splicing systems indispensable.
- Corrugated Boxes and Cartons: Large-scale production of corrugated boxes and cartons utilizes automatic splicing to meet high volume demands efficiently.
Challenges in Implementing Automatic Splicing Systems
While automatic splicing systems offer significant benefits, there are a few challenges to consider:
- Initial Investment: These systems require an upfront investment, which may be substantial depending on the system’s complexity.
- Maintenance Requirements: Splicing systems must be maintained regularly to ensure sensors and other components are functioning optimally.
- Training Needs: Operators may need training to oversee the operation and troubleshoot issues as they arise.
Best Practices for Operating Automatic Splicing Systems
- Regular Sensor Calibration: Sensors are critical for detecting roll status; regular calibration ensures they provide accurate data.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including checking adhesives, tension control, and alignment systems, helps prevent operational issues.
- Operator Training: Provide operators with training to handle minor troubleshooting, so they can resolve issues quickly if they arise during production.
Emerging Innovations in Automatic Splicing Technology
As flexographic printing evolves, so do splicing technologies. Some notable innovations include:
- Smart Sensors with IoT Integration: IoT-enabled sensors allow for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime.
- AI-Powered Tension Control Systems: Artificial intelligence optimizes tension control to improve splice quality and prevent substrate tearing.
- Eco-Friendly Adhesives: Advances in eco-friendly adhesive options are making splicing systems more sustainable, aligning with industry efforts to reduce environmental impact.
FAQs
What is an automatic splicing system?
An automatic splicing system enables continuous substrate feed in flexographic printing by joining a new roll with the expiring one without stopping the press.
How does a flying splicing system differ from a zero-speed splicing system?
Flying splicing systems splice at high speeds without pausing the press, while zero-speed systems momentarily stop the web but maintain press speed.
What are the benefits of using automatic splicing systems in flexography?
Automatic splicing systems reduce downtime, waste, and improve productivity by allowing uninterrupted production runs.
Do automatic splicing systems require special maintenance?
Yes, regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal function, including sensor calibration and tension control checks.
What types of substrates can automatic splicing systems handle?
Automatic splicing systems can handle various substrates, including plastic films, paper, and other flexible materials common in flexography.
Can automatic splicing systems improve print quality?
Yes, by maintaining consistent tension and alignment, splicing systems help ensure print quality remains high throughout long print runs.
Conclusion
Automatic splicing systems have become indispensable in modern flexographic printing, enabling high-speed, continuous operations that minimize waste and downtime. By automating the roll-changing process, these systems improve productivity and print consistency, making them essential for businesses aiming to optimize their flexographic workflows. As innovations in splicing technology continue, flexography will only become more efficient, flexible, and capable of meeting the demands of high-speed, high-quality printing.