Making flexo printing plates is indispensable in the production of packaging materials and labels, demanding a rigorous production process. By leveraging cutting-edge Flexo Imaging Technology, the manufacturing of these plates incorporates precise steps, ensuring superior results. The integration of rubber-based materials into this process marks a significant advancement, offering durability and allowing for minimal post-processing compared to zinc plates in traditional printing.
These plates find diverse applications across the industry, from printing labels on bottles and cans to creating seals for packaging boxes and shipping containers. Their versatility and efficacy make flexo plates indispensable tools in the printing and packaging sectors.
Flexo Plate Making with Flexo Imaging Technology
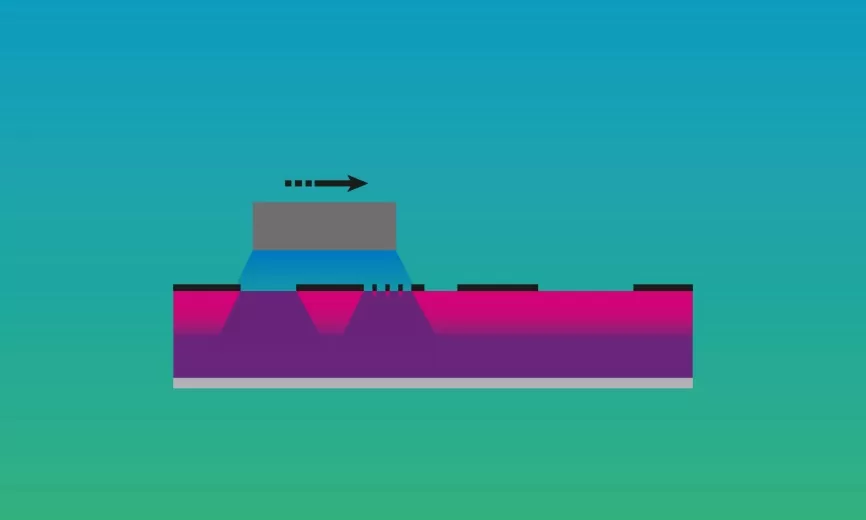
The process begins with a rubber-based digital polymer plate, signifying a blend of flexographic innovation with traditional printing principles. A meticulous back exposure sets the stage before the plate enters a digital flexo imaging device. Here, a laser carefully engraves the image onto the plate at the desired resolution. UV main exposure follows, using a UV light-array within the imaging device to harden the plate selectively.
Flexo plates benefit from the robustness of rubber and filler content, which can be adjusted to achieve the perfect hardness. This customisation reduces the reliance on expensive machinery and chemicals, streamlining the production process. Commercial flexo machines, though possibly costing up to $40,000, exemplify how quality plates can be produced more economically.
Detailed Steps in Flexo Plate Making Process
It’s important to note that flexographic plates comprise a dual-layer structure of rubber materials. The composition includes a softer top layer paired with a firmer bottom layer. This arrangement allows for a balance of flexibility and stability in the plate design. The softer upper layer consists of soft silicone rubber, known for its superior pliability compared to traditional rubber. This layer can be heated to modify its properties.
1. Design Creation and Transfer
The journey begins with design creation, where skilled designers utilise software like Adobe Illustrator, translating intricate concepts into digital artwork for precise replication. Following design finalisation, a meticulous transfer process conveys the design onto a transparent film or specialised plate material through photopolymer platemaking to ensure accuracy and fidelity in image reproduction.
2. Plate Preparation and Exposure
Essential for optimal functionality, plate preparation includes thorough cleaning to eliminate contaminants, enhancing ink adhesion during printing. The subsequent exposure phase involves subjecting the plate to UV light, hardening specific areas to form raised image elements vital for ink retention.
Before starting, ensure you have a light box ready for exposing the flexo printing plate, as it’s crucial for the process. Exposing the plate on the light box allows light to penetrate and reveal the negative areas necessary for printing. Incorrect exposure can render the plate ineffective.
3. Development and Post-Processing
Post-exposure, after removing the plate from the light box, the development phase commences, washing away unexposed areas by a developing solution, typically water, to stabilise the emulsion on the film, leave behind the raised images, and enhance transparency.
A combination of drying and treatment with UVA and UVC light ensures the plate’s resilience and longevity. The incorporation of soft silicone rubber as the top layer of the plate highlights a unique approach, enhancing the plates’ functionality for specific applications.
4. Mounting and Ink Application
Precision in mounting the developed plate onto a printing cylinder is crucial for alignment. The raised areas receive ink, which then transfers to the substrate material as the cylinder rotates within the printing press.
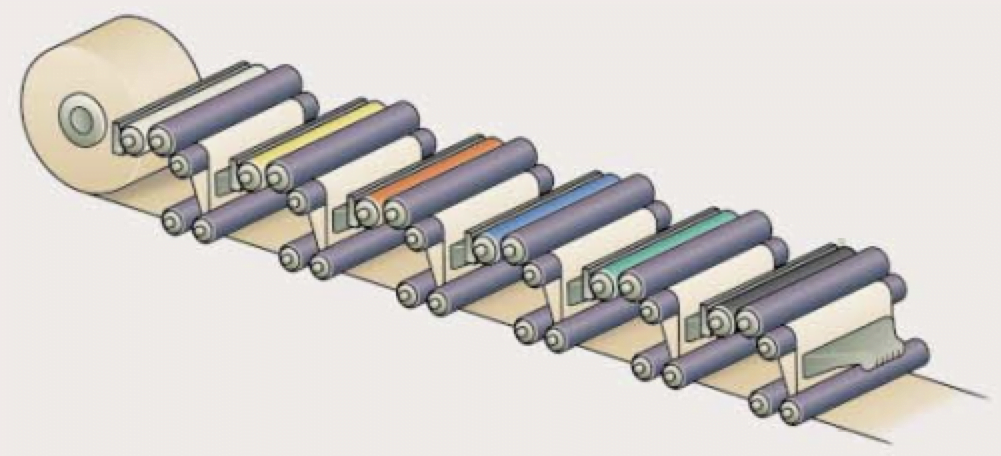
5. Printing Process and Quality Control
Quality control is imperative throughout the printing process, maintaining high standards in colour accuracy, sharpness, and overall quality of the printed material. Flexo plates, known for their durability and versatility, cater to a broad spectrum of applications including labels, flexible packaging, corrugated materials, and can decoration.
Conclusion
Flexographic plates have a longstanding history in the industry, serving essential functions in printing texts on paper and producing plastic labels and signage. Their robustness and user-friendly nature make them a preferred choice. Flexo plates can be crafted from various materials, offering flexibility in their application.
Flexographic plate making technology not only underscores the adaptability of rubber-based materials but also showcases the potential for customisation in plate hardness and application specificity. The preparation and handling of these plates demonstrate a seamless blend of traditional craftsmanship and modern technology, ensuring the delivery of high-calibre printing plates critical for the flexographic printing process.
Flexo plate production embodies a meticulous sequence of steps aimed at crafting premium printed materials for diverse applications. This integrated approach, combining the durability and flexibility of rubber materials with advanced imaging technology, epitomises the evolution of flexographic printing plate manufacturing.