A highly versatile and efficient printing process used in a wide range of industries, flexographic printing benefits significantly from the use of advanced inks whose formulations offer vibrant colours, durable finishes and compatibility with a wide range of substrates, including flexible packaging and corrugated board. These flexo printing inks can be solvent- or water-based, or for UV inks, which employ a radiation-curing mechanism. They contain colour pigments, binders, solvents, auxiliaries, and additives, with photo-initiators added in UV inks. The diversity of ink systems in flexographic printing is essential due to their specific applications and the need for inks that excel in different scenarios, largely determined by their respective features.
This article delves into the various types of flexo printing inks, discussing their distinct applications, market shares, and the indispensable role that additives play in improving ink performance.
Types of Flexo Inks, Their Applications and Market Shares
Flexographic printing has evolved significantly, with inks engineered for specific applications and substrates to meet the needs of specific segments, resulting in optimal print quality and efficiency across the diverse print market.
Water-Based Inks
Water-based inks, known for their eco-friendliness and safety, contain pigments or dyes in a water-soluble base, making them highly popular across Europe, where they account for about a 15% share of the market, primarily in the non-food sector.
Their low VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) emissions and ease of cleanup make them the preferred choice for printing on paper, corrugated board applications, and especially in the food sector for flexible packaging, due to the minimal requirement for volatile solvents. The printing market is especially in favour of these inks for their environmental compliance, crucial for products like food packaging.
Additionally, water-based inks are the preferred choice for printing on corrugated board, representing nearly 100% of usage in this area, owing to their superior drying characteristics on absorbent substrates, and they also feature a wide application in printing plastic carrier bags, highlighting their versatility and growing acceptance in applications demanding sustainability and safety.
Solvent-Based Inks
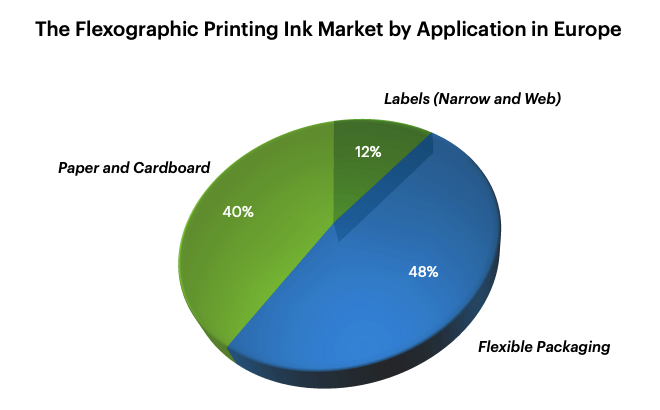
Solvent-based inks, comprising pigments suspended in a solvent polymer solution, are renowned for their superb adhesion to non-porous substrates such as plastics and foils, making them a cornerstone in the realm of flexible packaging where they boast a commanding 80% usage share. Celebrated for their rapid drying times, durability, and resistance to rubbing and scratching, these inks are particularly suited for packaging materials that endure significant wear and tear during shipping and handling.
A notable and versatile category within this ink type utilises nitrocellulose (NC) as the foundational binder, while the recent rising adoption of polyurethane-based inks (PUR) marks a significant evolution, with these two ink systems complementing each other’s strengths—NC-based inks are favoured for surface and lamination printing, whereas PUR inks excel in demanding applications such as the pasteurisation and sterilisation of food items, where NC variants fall short.
Furthermore, solvent-based inks are also pivotal in label printing, securing a 15% market share, predominantly for use on plastic films. This highlights their lesser, yet critical role compared to their dominance in flexible packaging, with water-based ink systems trailing behind in label printing, applied to both film materials and absorbent substrates.
UV and LED UV Inks
UV-curable inks, which harden or cure upon exposure to ultraviolet light, instantly drying, enjoy a specific but significant niche in the printing industry, with their adoption primarily dominated by label printing, where they constitute approximately 80% of ink technology used. This is in contrast to their limited application in flexible packaging, where they account for only about 5% due to concerns over their potential for migration.
These inks, favoured for their ability to adhere to a diverse array of materials, quick drying times, high gloss, and contribution to superior print quality featuring vibrant colours, are compatible with a wide variety of substrates including plastics, papers, and metals. Particularly in high-speed printing operations and for products needing strong resistance to chemicals and abrasion, UV-curable inks are the preferred choice.
Despite their higher cost, both UV and the more recent innovation, LED UV inks, which cure under energy-efficient LED UV lights offering reduced energy consumption and heat emission, are making inroads into high-end and specialty printing sectors thanks to their excellent quality and versatility. The driving force behind the increasing demand for these inks is the expansion of the flexible packaging market, spurred by the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries, highlighting the importance of UV-curable inks in modern printing applications.
 © Anyflexo
© AnyflexoInk Additives and Their Functions
Additives play a pivotal role in flexo printing inks, enhancing their performance and compatibility with different printing conditions and substrates.
- Defoamers: Essential in water-based inks, defoamers prevent foam formation during printing, ensuring even ink distribution and high-quality prints.
- Wetting Agents: These additives improve the ink’s wetting properties, ensuring better adhesion to the substrate and more uniform ink lay-down.
- Rheology Modifiers: Used to adjust the ink’s viscosity, rheology modifiers ensure smooth ink flow and transfer from the anilox rollers to the printing plate and ultimately to the substrate.
- Slip Agents: Applied in inks for film and other non-porous substrates, slip agents enhance the ink’s ability to glide over surfaces, reducing friction and scratching.
- Photo-Initiators: Specific to UV-curable inks, photo-initiators initiate the curing process under UV light, enabling rapid drying and curing of the ink.
The deliberate selection and incorporation of these additives are crucial in tailoring the ink’s performance to meet the specific demands of each printing application, ensuring efficiency, durability, and high-quality outcomes.
In Conclusion
Flexo printing inks are an essential component of the flexographic printing process, with their variety and technological advancements driving the industry forward. From water-based to UV-curable inks, each type has its niche, determined by substrate compatibility, application requirements, and environmental considerations. Furthermore, the strategic use of ink additives enhances their performance, ensuring that flexo printing remains a versatile, efficient, and high-quality printing option. As the flexo industry continues to grow and evolve, so too will the development and refinement of flexo printing inks, promising even greater possibilities and applications in the future.