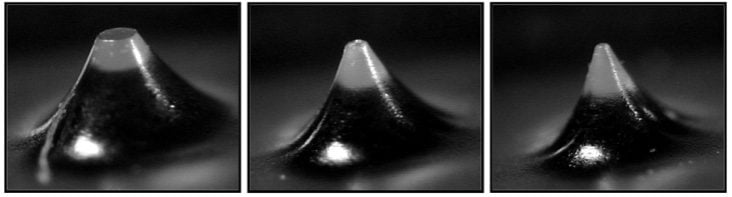
Halftone dots of a flexographic printing plate in different diameters (source: DFTA)
What are flexographic printing plates?
Flexographic printing uses elastic, flexible printing plates that are necessary to adapt to the structure of rough and uneven substrate surfaces. Their job is to transfer the ink from the anilox roller to the substrate. Where are flexographic printing plates used and what are the differences? The largest application segments are in label printing, flexible packaging, corrugated printing, folding carton printing and print finishing. In these segments, very different properties are required depending on the material, which is why the plates differ in their thickness, hardness, swelling resistance and ink transfer.
Label Printing
The flexographic printing plates usually have a thickness of 1.14 or 1.70 mm. If used with UV inks, the plate must be as swell-resistant as possible. Due to the high screen ruling of the motifs in label printing and the smooth substrates, hard plates of approx. 60° ShA (DIN) are mainly used.
Flexible Packaging
The usual flexographic plate thickness in the flexible packaging is 1.14 mm thick. In addition to these thin plates, conventional plate thicknesses of 2.54 and 2.84 mm are also used. In printing, they must be resistant to alcoholic solvents as well as to acetates to the greatest possible extent. For flexographic printing on packaging films, mainly hard plate types are used, similar to label printing. For more porous or rough substrates such as paper, medium-hard flexo plates of 40 – 50° ShA (DIN) are common.
Corrugated Board
For direct printing on corrugated board are soft, thick flexographic plates of approx. 25 – 40° ShA (DIN) used, which adapt better to the corrugated structure of the substrate. They must have good ink transfer with water-based inks in order to print solid areas in a closed manner. Their flexo plate thickness is usually between 3.94 and 6.35mm. Here, too, the trend is toward harder, thin plates 2.84 mm thick and below, which are mounted on compressible foam mats as a substructure. They significantly reduce the washboard effect that occurs in corrugated printing.
Folding Carton Printing
Depending on the quality of the cardboard and its coating, medium-hard to hard flexographic plates are used in folding box printing, which have good ink transfer with water-based inks.
Print Finishing
The plates in this area of application are also medium-hard to hard, have a thickness of 1.16 mm and must be resistant to print runs with UV printing varnishes.
So how does the print motif get onto the printing plates? Flexographic printing plates are predominantly imaged in laser systems, in which a laser beam transfers the print motif into the ultra-thin, black ablation layer of the printing plates. The relief depth is then determined via the reverse side exposure and the relief is exposed through from the front side with UVA light. During washout, the unexposed parts are removed and the relief, which was previously only latent, is exposed. After drying, the plates are ready for mounting and arrive at the flexographic presses on printing cylinders, sleeves or mounting carrier sheets ready for printing.
The duration of plate production is a crucial factor that heavily relies on the solvent used for washing out the plates. The duration is longest when using solvent-based washout solutions, as the polymer layer swells significantly and requires drying. However, it is shorter when using water-washable plate systems, which only cause slight swelling. The duration is even shorter for thermal systems, where the plates do not require washing out. In this process, the non-cross-linked polymer is removed by heating it with a non-woven material. This ensures that no swelling occurs.