Flexographic printing demands high precision to maintain image alignment, color accuracy, and print quality across substrates and speeds. Register control mechanisms are essential tools to ensure this level of accuracy, helping printers correct misalignments automatically or manually. This guide offers an in-depth look into the significance of register control in flexographic printing, the different types of systems available, and their benefits.
Introduction to Register Control in Flexography
In flexographic printing, registration refers to the precise alignment of colors and images. Each color is printed in a different pass, and when the registers are out of alignment, images appear blurred, colors misalign, and print quality suffers. Register control mechanisms address these issues by aligning all print colors accurately on the substrate.
Why Register Control Mechanisms are Essential in Flexography
The precision of register control systems ensures that images printed in multiple passes remain aligned. This is crucial in flexography due to variables like substrate stretch, speed fluctuations, and temperature changes, which can all impact alignment. Without effective control mechanisms, print consistency and quality may degrade significantly, leading to waste and operational delays.
How Register Control Mechanisms Work
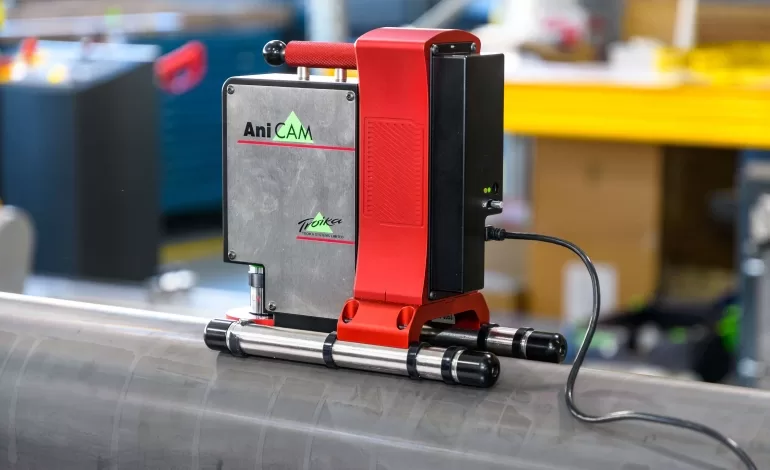
Register control mechanisms work by continuously monitoring print alignment during the production process. Sensors, cameras, or lasers detect any shifts in registration, comparing the actual printed image with the digital template. These mechanisms make real-time adjustments, maintaining alignment with precision.
Types of Register Control Mechanisms in Flexography
Manual Register Control
Manual control involves an operator adjusting alignment by observing and reacting to register shifts. This approach is often suitable for smaller jobs or older equipment.
Automatic Register Control (ARC)
Automatic systems use sensors and cameras to detect shifts and correct them autonomously. This method is faster and more accurate, ideal for high-speed, high-volume production.
Closed-Loop Register Control
Closed-loop systems provide continuous monitoring and feedback to maintain accurate alignment throughout the print run. Sensors detect misalignment, prompting adjustments without needing operator intervention.
Open-Loop Register Control
Open-loop systems work based on initial settings but do not provide continuous feedback, making them more suitable for simpler print jobs where precision is less critical.
Components of Register Control Mechanisms
Sensors
Sensors detect any shifts in the alignment, sending data to the control system for necessary adjustments. Optical and camera-based sensors are common, with the latter offering high-resolution monitoring for detailed control.
Cameras and Scanners
Modern systems use high-speed cameras that capture images in real time, detecting misalignments with high precision. Scanners may also be used, particularly in high-speed applications.
Feedback Systems
Feedback loops in closed-loop systems continuously send data back to the register control software, allowing for automatic adjustments based on real-time conditions.
Servo Motors
Servo motors make precise mechanical adjustments to realign print stations. Their fast, accurate movements are critical for maintaining register control at high speeds.
Benefits of Using Register Control Mechanisms
Enhanced Print Quality
Register control mechanisms provide the alignment needed for crisp, high-quality prints, particularly important in multi-color and high-definition printing.
Increased Production Speed
Automatic adjustments reduce downtime, allowing printers to maintain higher speeds without sacrificing quality.
Reduced Waste and Material Cost
By maintaining accurate registration, register control mechanisms minimize substrate waste and save costs related to materials and inks.
Consistency Across Print Runs
These mechanisms ensure consistency from one print run to the next, maintaining the same quality standards regardless of job size.
Choosing the Right Register Control System for Flexography
When selecting a register control system, consider factors such as:
- Production Speed: High-speed operations benefit from closed-loop, automatic systems.
- Substrate Type: Flexible substrates may need more sophisticated control mechanisms due to their tendency to stretch.
- Color Complexity: Multi-color jobs often require precise control for alignment across multiple print stations.
- Budget and Machine Compatibility: Advanced systems require an investment but yield quality improvements and operational efficiency.
Optimizing Register Control for Different Substrates
Paper Substrates
Register control mechanisms in flexography manage paper’s natural tendency to shift during production, minimizing the chance of alignment errors due to stretching or warping.
Plastic Films
Plastic films are more prone to stretch, requiring closed-loop or servo-driven systems to maintain registration under changing speeds or tension conditions.
Flexible Packaging Materials
Flexible packaging demands robust control due to high speeds, stretch-prone substrates, and the multi-layered nature of many packaging designs.
The Role of Automation in Modern Register Control Mechanisms
Automation has revolutionized register control by enabling precise, real-time adjustments. Fully automated systems are now capable of maintaining alignment without manual intervention, adjusting for even the smallest shifts caused by environmental factors or substrate changes. Automation also offers data collection features, helping operators fine-tune production over time.
Advanced Technologies in Register Control
Digital Sensors
These sensors enhance accuracy and sensitivity, allowing register control systems to detect minute deviations in alignment.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
Some register control systems now incorporate AI algorithms that predict alignment issues and make preemptive adjustments, reducing errors before they become visible.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Remote control systems allow operators to monitor and adjust register settings from a different location, ensuring uninterrupted production with minimal manual involvement.
Challenges in Implementing Register Control Mechanisms
Despite their benefits, register control mechanisms come with challenges. Installing new systems can be costly, and training is necessary to operate sophisticated, automated systems. Additionally, not all substrates are compatible with every type of register control, requiring careful system selection to avoid misalignment and waste.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Register Control Performance
To ensure register control systems function efficiently, regular maintenance is essential. Check sensors and cameras for accuracy, update software, and calibrate mechanical parts to avoid malfunctions that may affect alignment.
Future Trends in Register Control for Flexography
With advancements in AI and machine learning, future register control systems will be more intuitive, capable of learning from print history to improve performance. Integration with broader automation frameworks will allow these systems to work seamlessly within larger production workflows.
FAQs
What are register control mechanisms?
Register control mechanisms are systems used in flexographic printing to align colors and images accurately, preventing misalignments.
How do automatic register control systems work?
Automatic systems use sensors or cameras to detect alignment shifts, making real-time adjustments to maintain consistent registration.
What’s the difference between closed-loop and open-loop register control?
Closed-loop systems continuously monitor alignment, adjusting as needed, while open-loop systems rely on initial settings and don’t offer feedback during printing.
Why is register control important in flexography?
Register control ensures color and image alignment, which is essential for quality in multi-pass, high-speed flexographic printing.
Can register control systems reduce waste?
Yes, by maintaining alignment, register control systems reduce material waste, especially on complex, multi-color jobs.
What factors should I consider when choosing a register control system?
Consider factors like production speed, substrate type, color complexity, and your budget to choose the right system.
Conclusion
Register control mechanisms are indispensable in flexographic printing, maintaining the alignment and quality essential for competitive, efficient production. Whether choosing basic manual controls or sophisticated closed-loop systems, the right register control mechanism can transform print quality, reduce waste, and enhance productivity across flexographic applications.





![[Flexo Flaw Fixing] Minor Defects](https://flexopedia.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/060_Minor_Defects-jpeg.webp)